Background
Reciprocating pumps (including diaphragm pumps, plunger pumps, and other
positive displacement pumps) are used in many applications, including
petroleum production facilities and refineries. Interactions with
connected pipelines and system parts must be taken into consideration as well
as system optimization with correct sizing of pulsation dampeners.
A Pulsation Analysis and mechanical review of piping
system is often necessary for new or existing reciprocating pumps systems to
avoid typical problems such as:
- excessive
pressure pulsations and piping vibration;
- pressure pulsation-induced cavitation;
- undesired
opening of PSVs due to pulsations;
- fatigue
failures to pipelines and components;
Scope
An acoustic analysis is recommended to optimize
overall system design by investigating the interaction between the pump and
pipeline with the following advantages:
– Reliable long-term operation: complying with defined
limit values for pressure pulsation and extending the service life of the
overall system;
– Increasing availability: Improving operating
reliability and lowering maintenance costs
Pulsation dampeners design options:
Our experience as a dampener manufacturer and acoustic
analysis engineering provide the best recommended options over our wide range
of products for a safe pumping system operation. Focusing on existing or new
pulsation dampeners installation performances.
If a preliminary piping layout is available as well as
pump and liquid information, a preliminary computation of static suction head
and pressure pulsations in the system, allow to select the correct pulsation
dampener (size and type). Similarly at discharge static pressure is generally
high and pulsations shall be lowered by suitable pulsation control to get
acceptable piping vibrations and avoid pressure safety valve chattering.
Calculation methods:
Two level of efforts are available according to API
674 STANDARD: Approach 1 and Approach 2.
Both methods use a state-of-the-art numerical
calculation method performed in Fox engineering department.
Design Approach 2
An acoustic system is modeled with detailed piping
drawings, liquid properties and equipment information. Peak-to-Peak Pulsation
Levels are calculated at the operating conditions and pump pressure steps are
chosen to yield the highest expected pulsation amplitudes throughout the piping
system. Pulsation amplitudes are then compared to the levels identified in API
674.
Pulsation-Induced Shaking Forces (Unbalanced Forces)
are calculated to predict the maximum pulsation-induced shaking forces and
unbalanced pressure acting on the critical elements of the piping system, such
as pulsation control devices, pulsation control device internals, vessels,
closed-end headers.
Piping Modifications are developed in the model if the
pulsation analysis indicates that pulsation levels and/or shaking forces are
excessive; modifications to the pulsation control devices and/or piping systems
are made and the analysis continued until the system meets the guidelines
defined in C.1.5 or other criteria as agreed upon by the Purchaser and Vendor.
A simple mechanical review shall be performed using
span and vessel mechanical natural frequency calculations to avoid mechanical
resonance. This review shall result in a table of various pipe sizes that
indicates the maximum allowable span (based on the maximum pump operating
speed) between piping supports as a function of pipe diameter, and the
separation margin requirements of API 674.
Design Approach 1
This simplified analytical study includes the design
of a pump pulsation suppression device using proprietary and/or empirical
analytical techniques to meet the pulsation levels specified in API 674 This
approach includes the study, good piping layout, good support/restraint
principles, and adequate NPIP to design a pulsation solution.
Model is generated in accordance with a simple
schematic diagram made available by the client. No extensive piping drawings
are required. This method provides a good quantitative overview of the basic
pressure pulsation behavior in the pipeline and pulsation dampener sizing.
Calculations and practice:
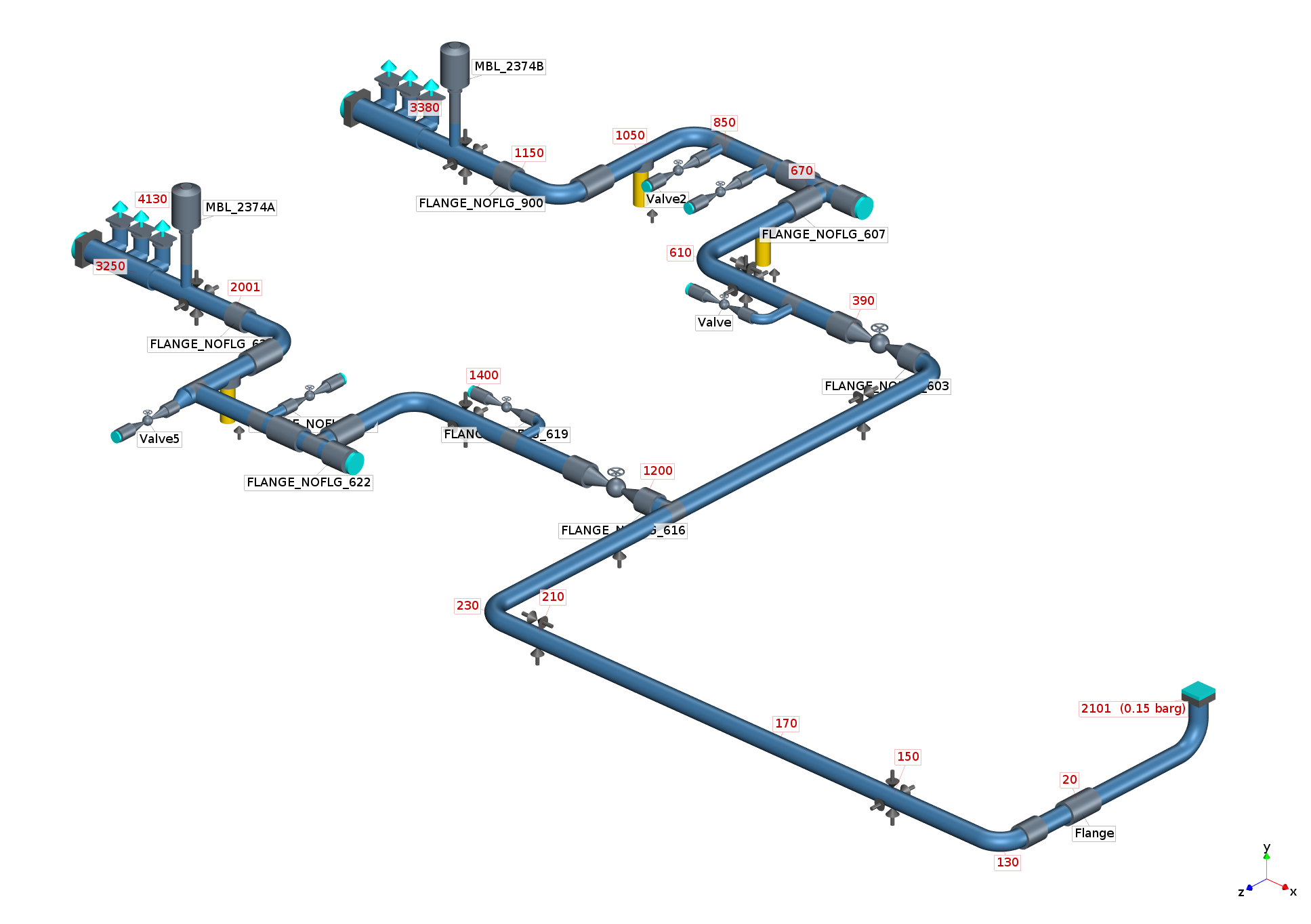
Suction system
model
Analysis:
simulation without pulsation dampener
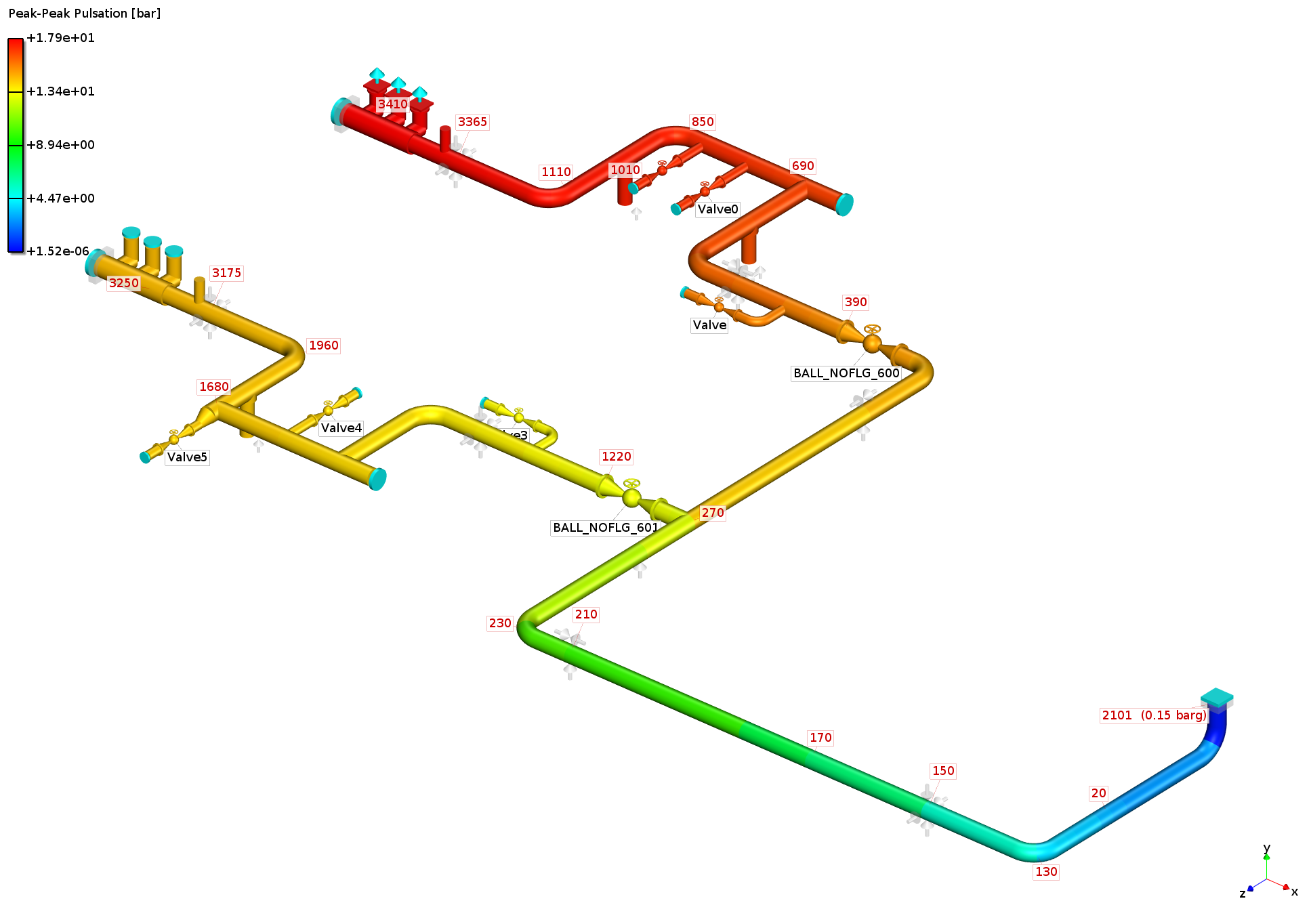
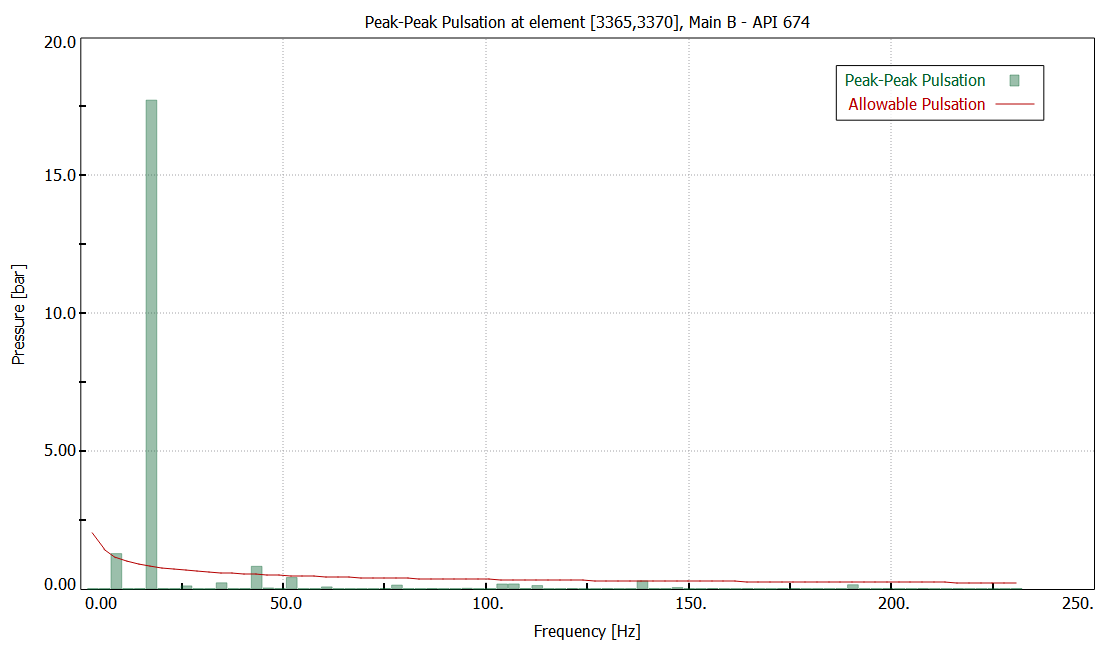
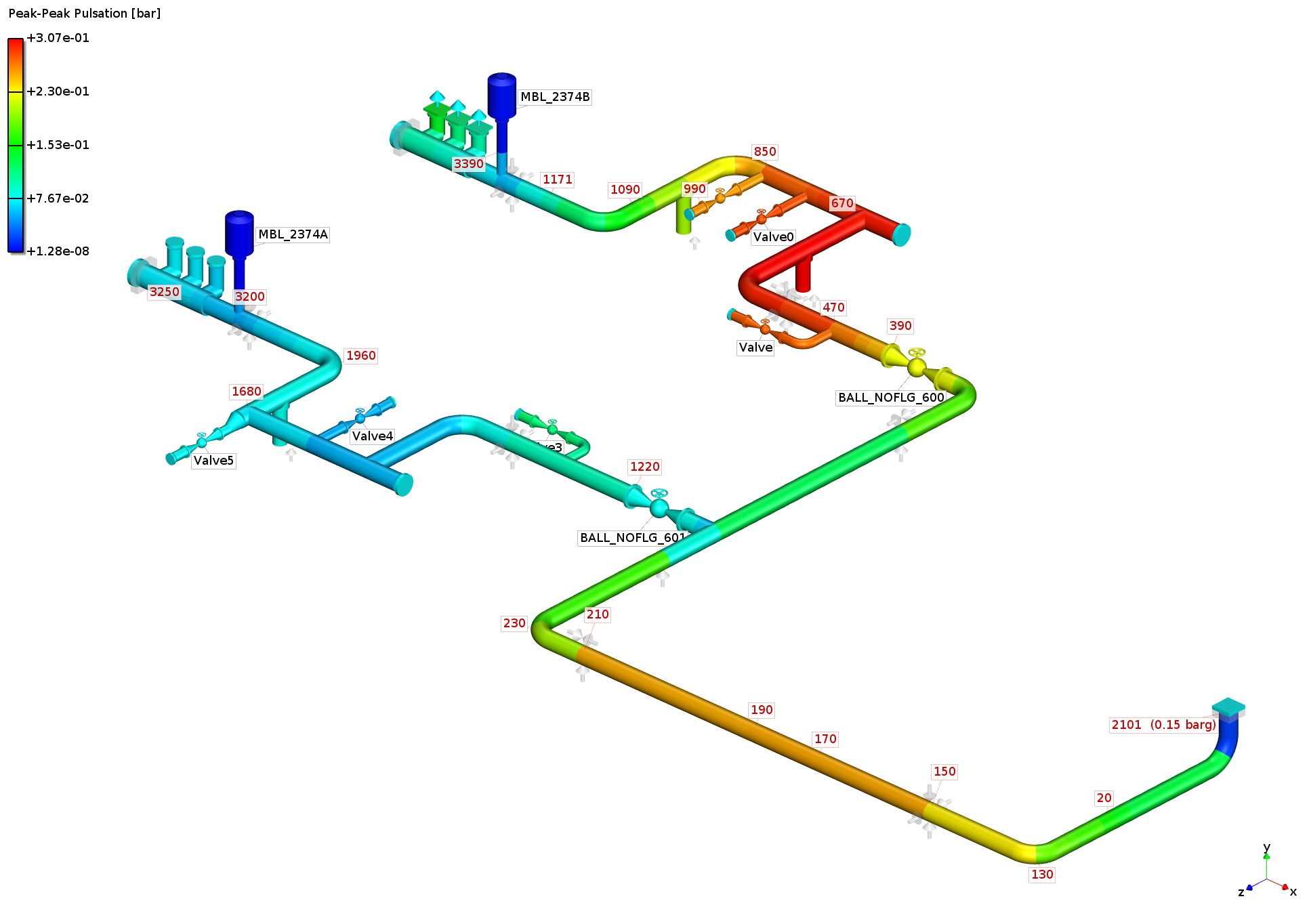
Analysis:
simulation with optimum dampener configuration
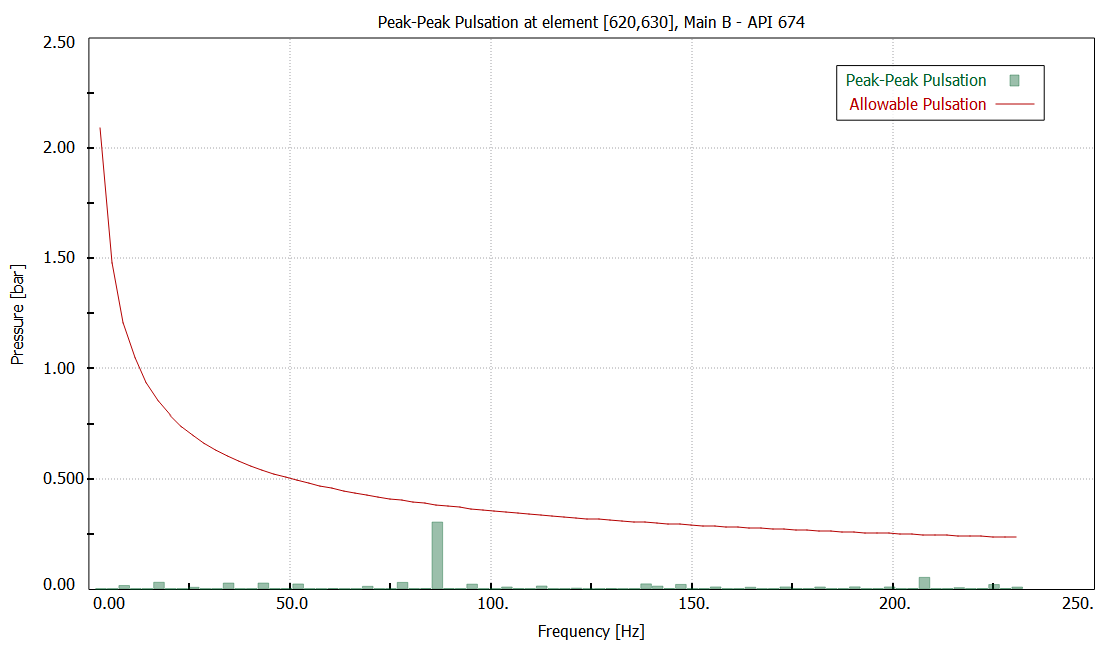
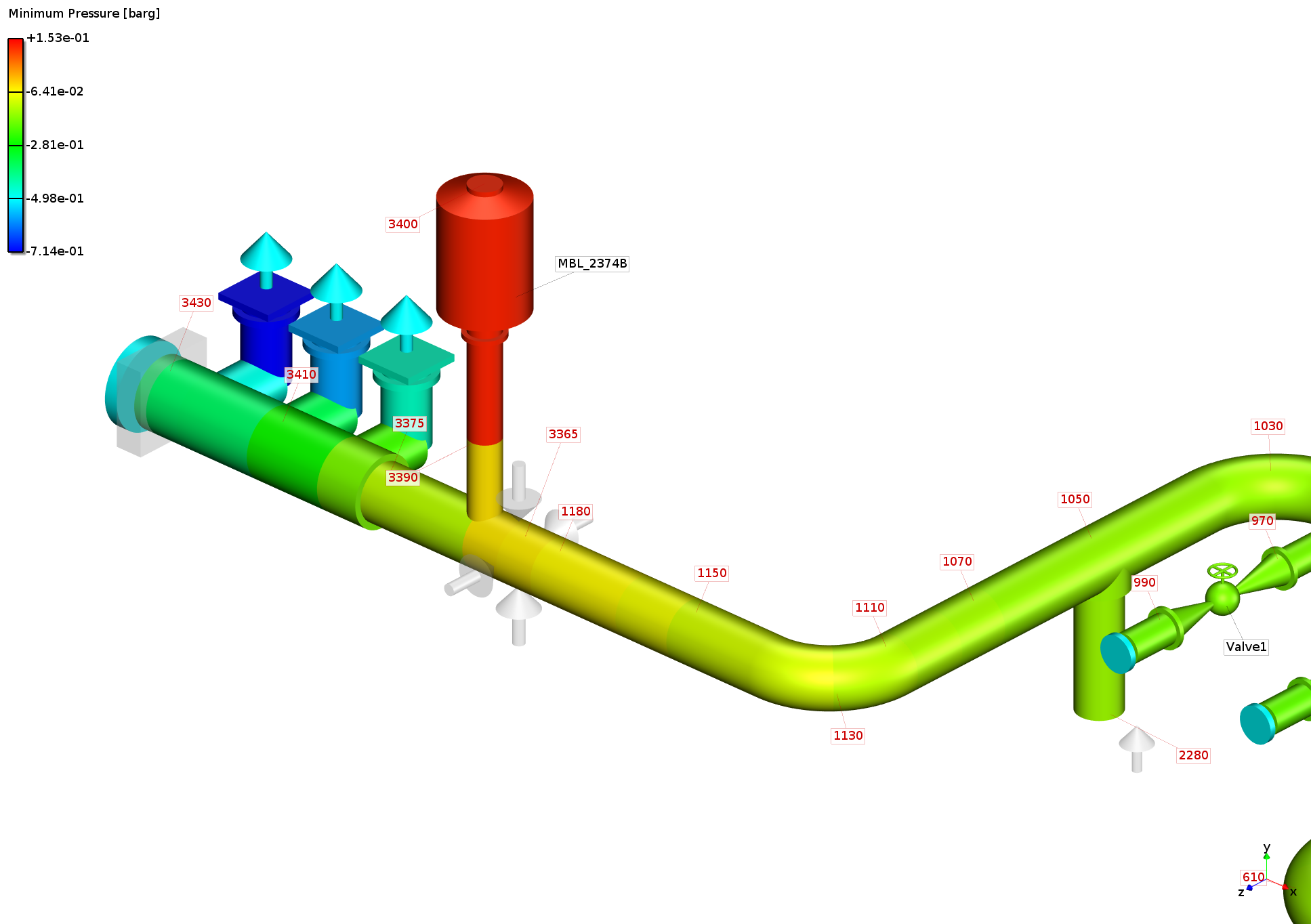
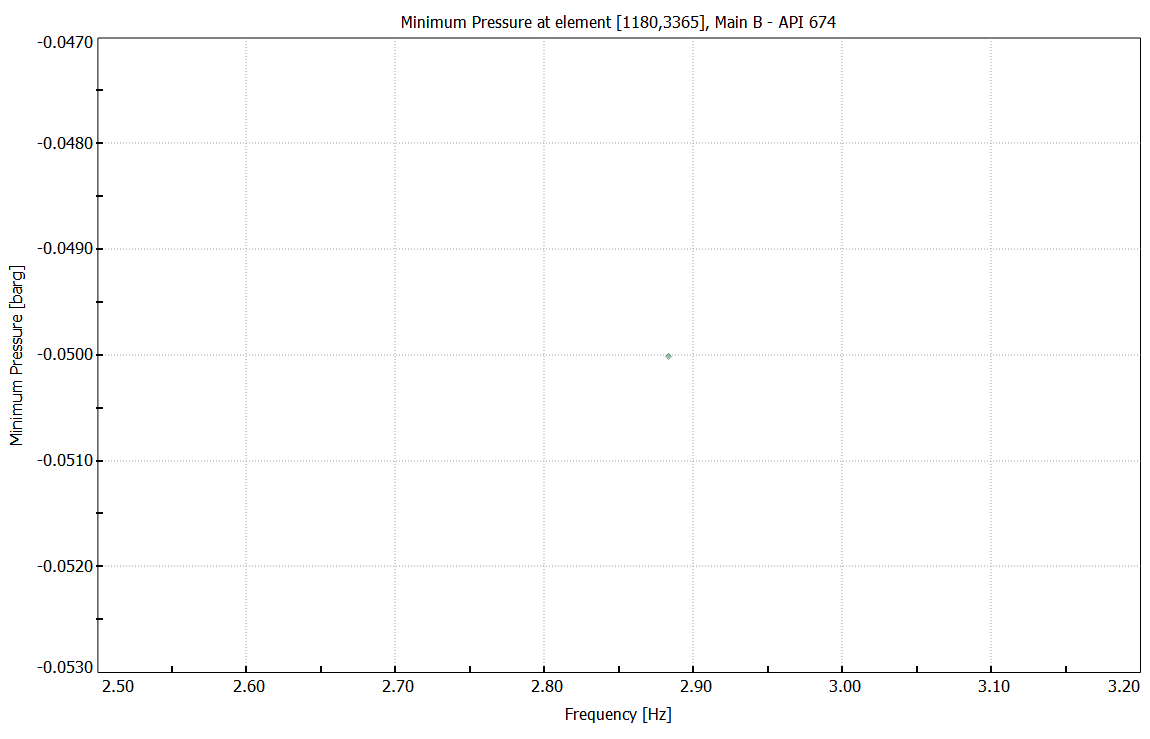
Minimum pressure at pump inlet port
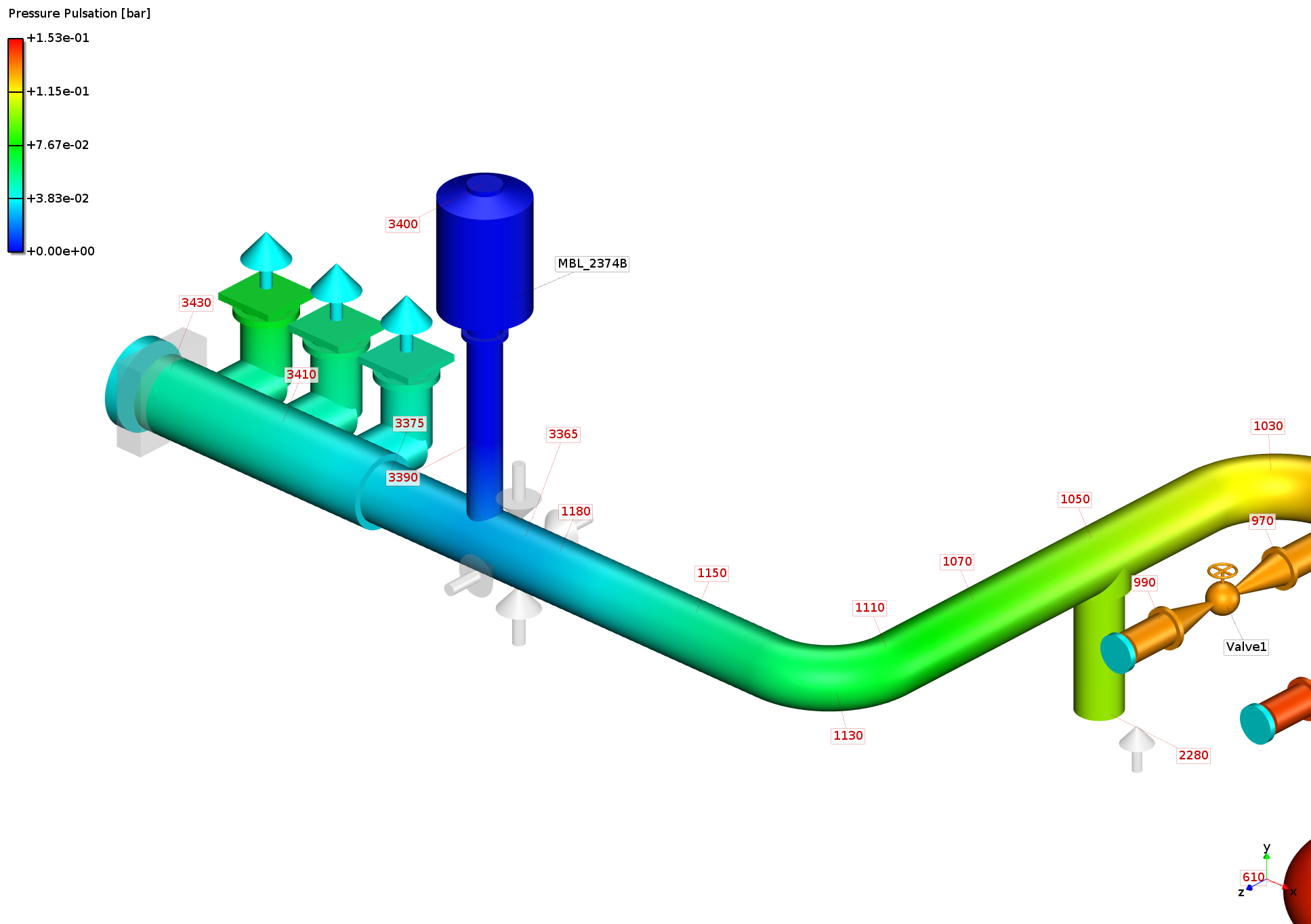
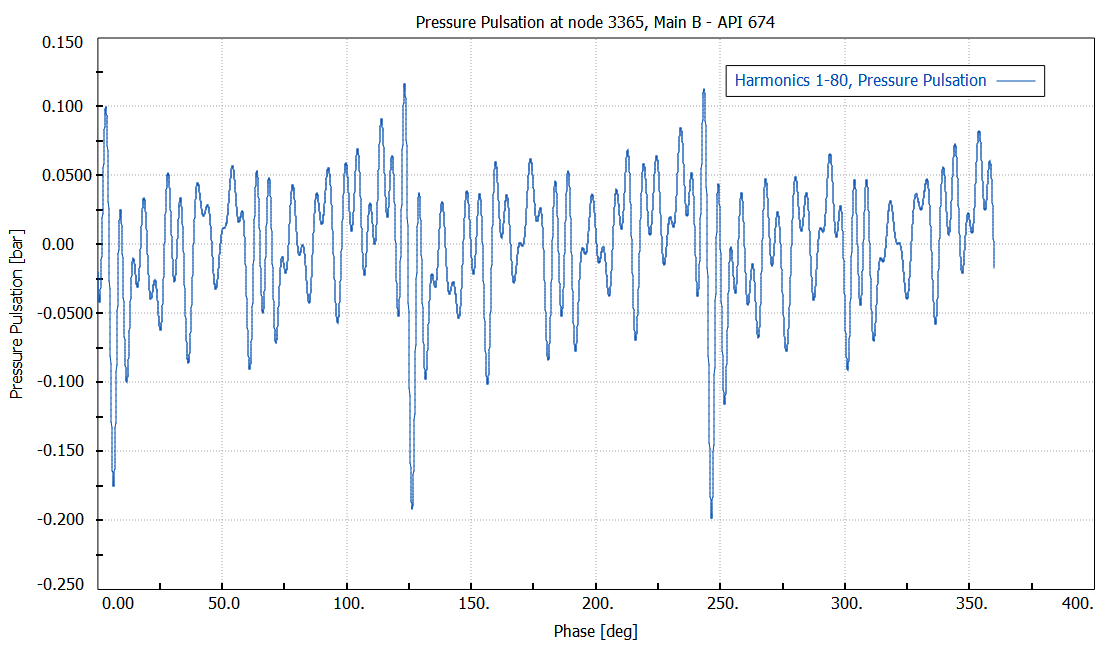
Pressure
pulsation at pump inlet port
--
Analysis:
simulation with variable speed pump
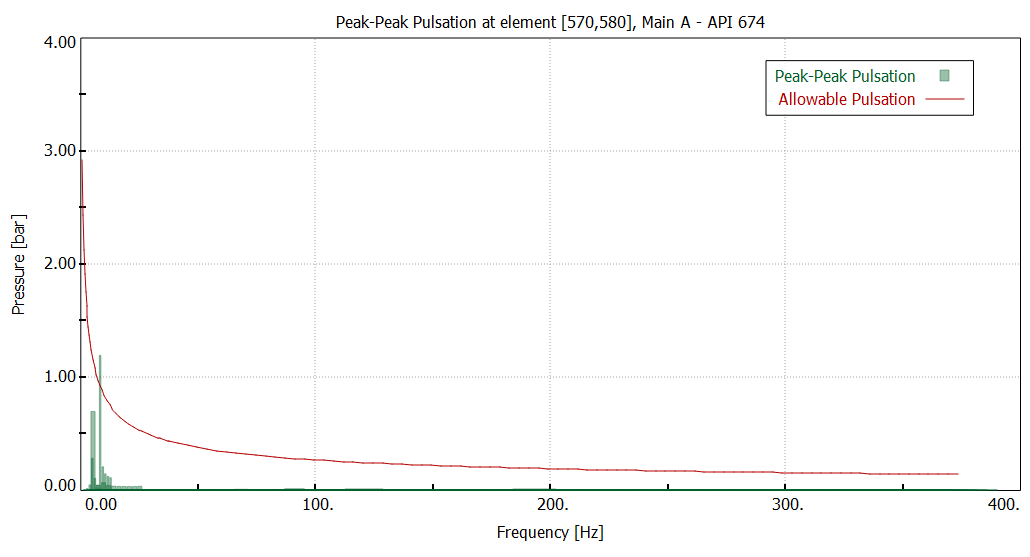
Analysis:
cavitation time [%] over speed range
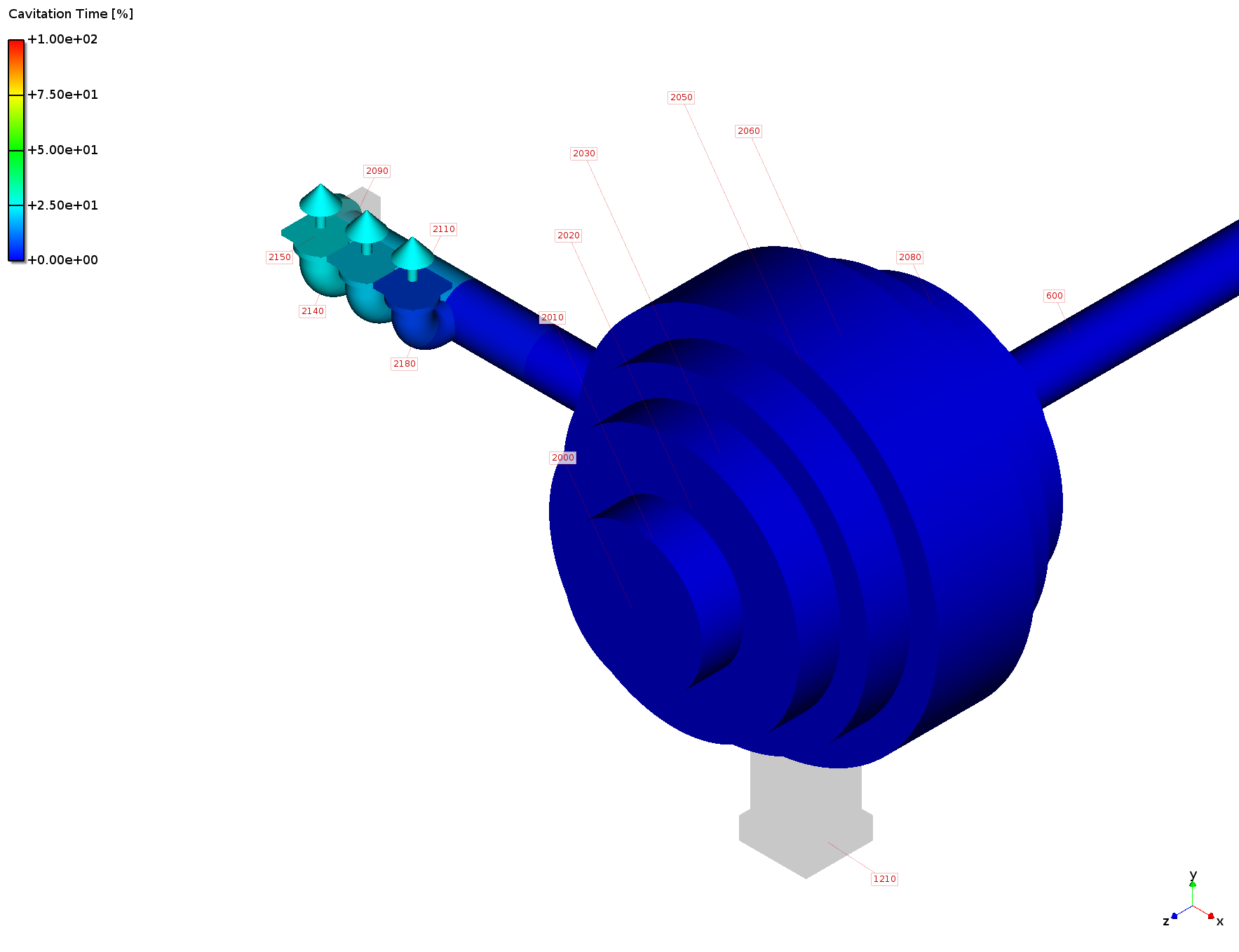
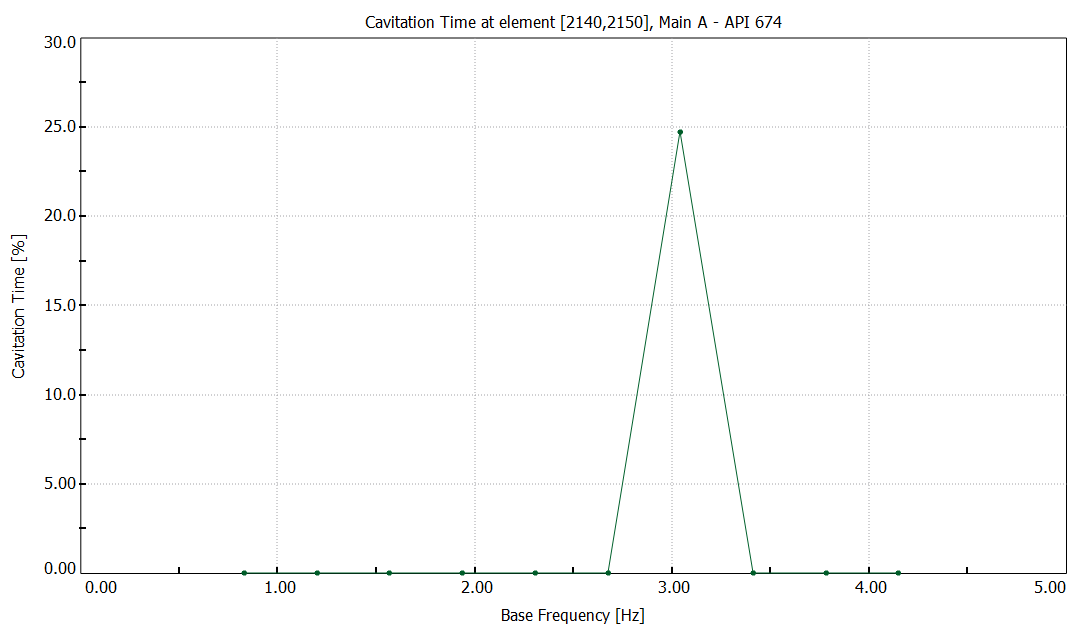
--
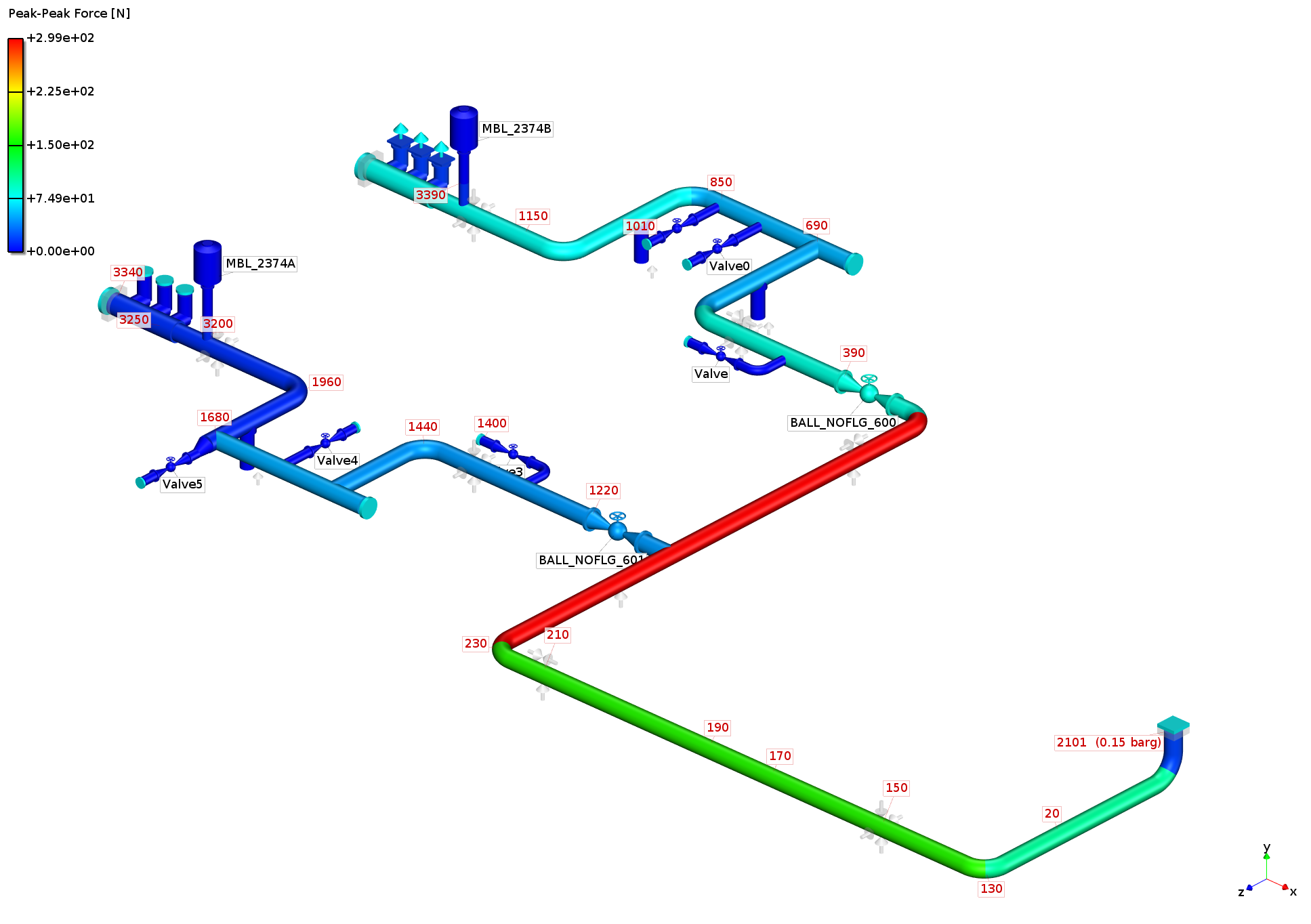
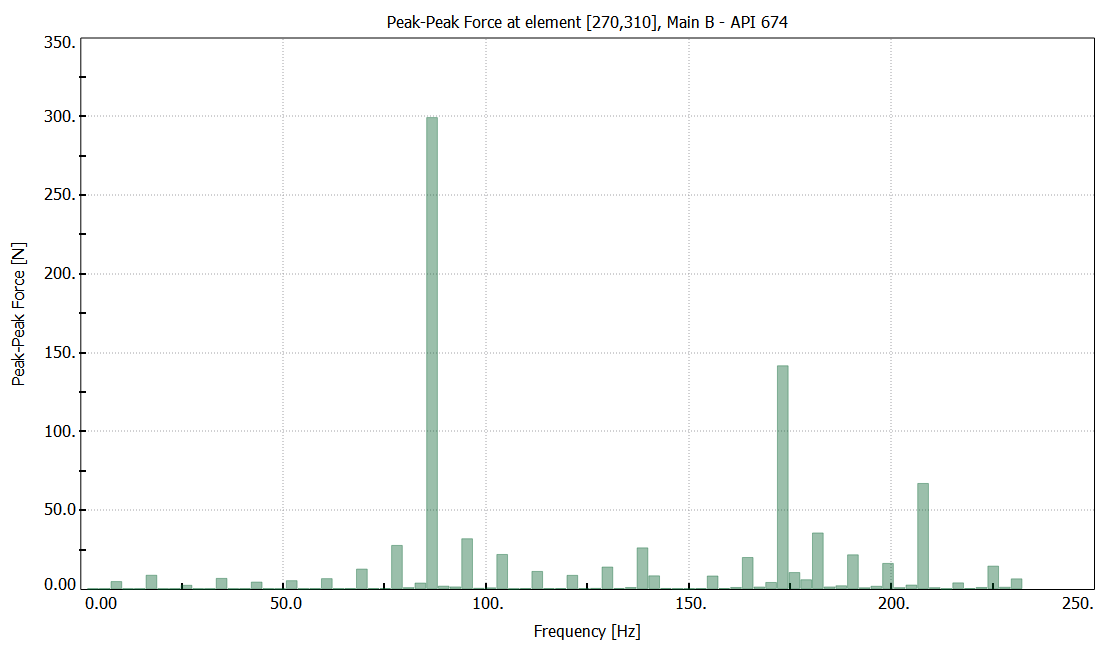
Force [N]
Spectra with pulsation dampeners
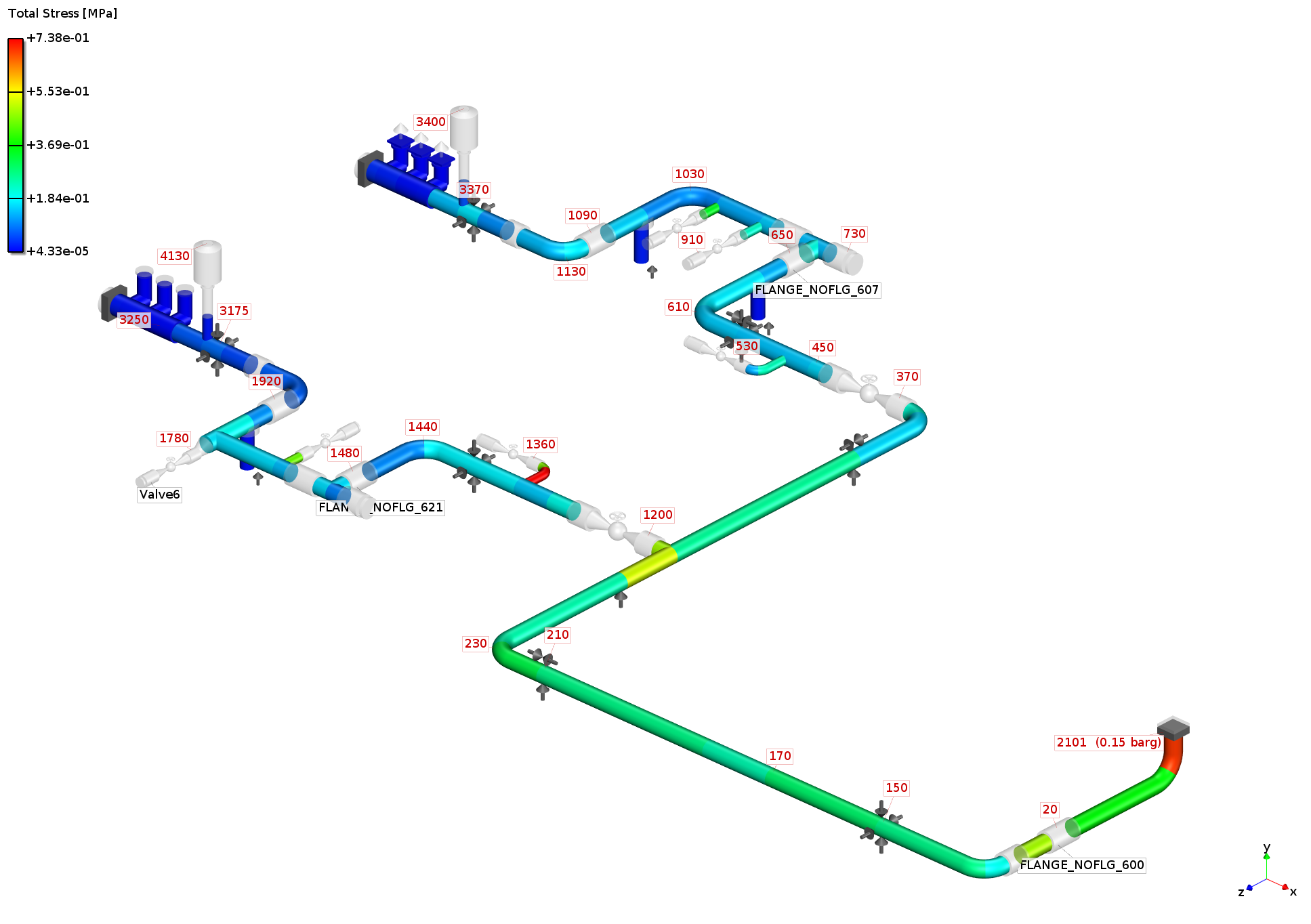
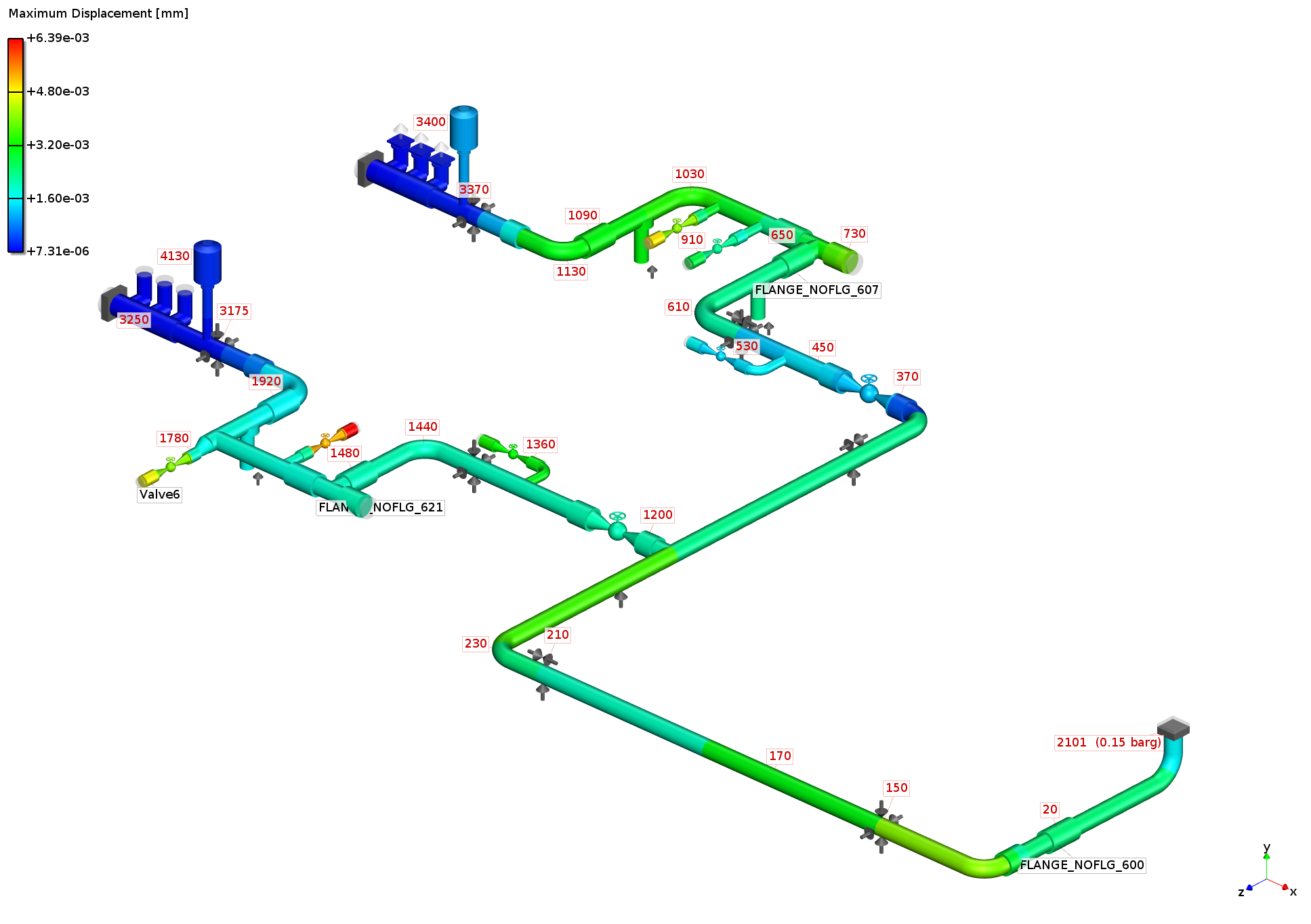
Analysis: Total
Stress and total displacement induced by acoustic pressure pulsations
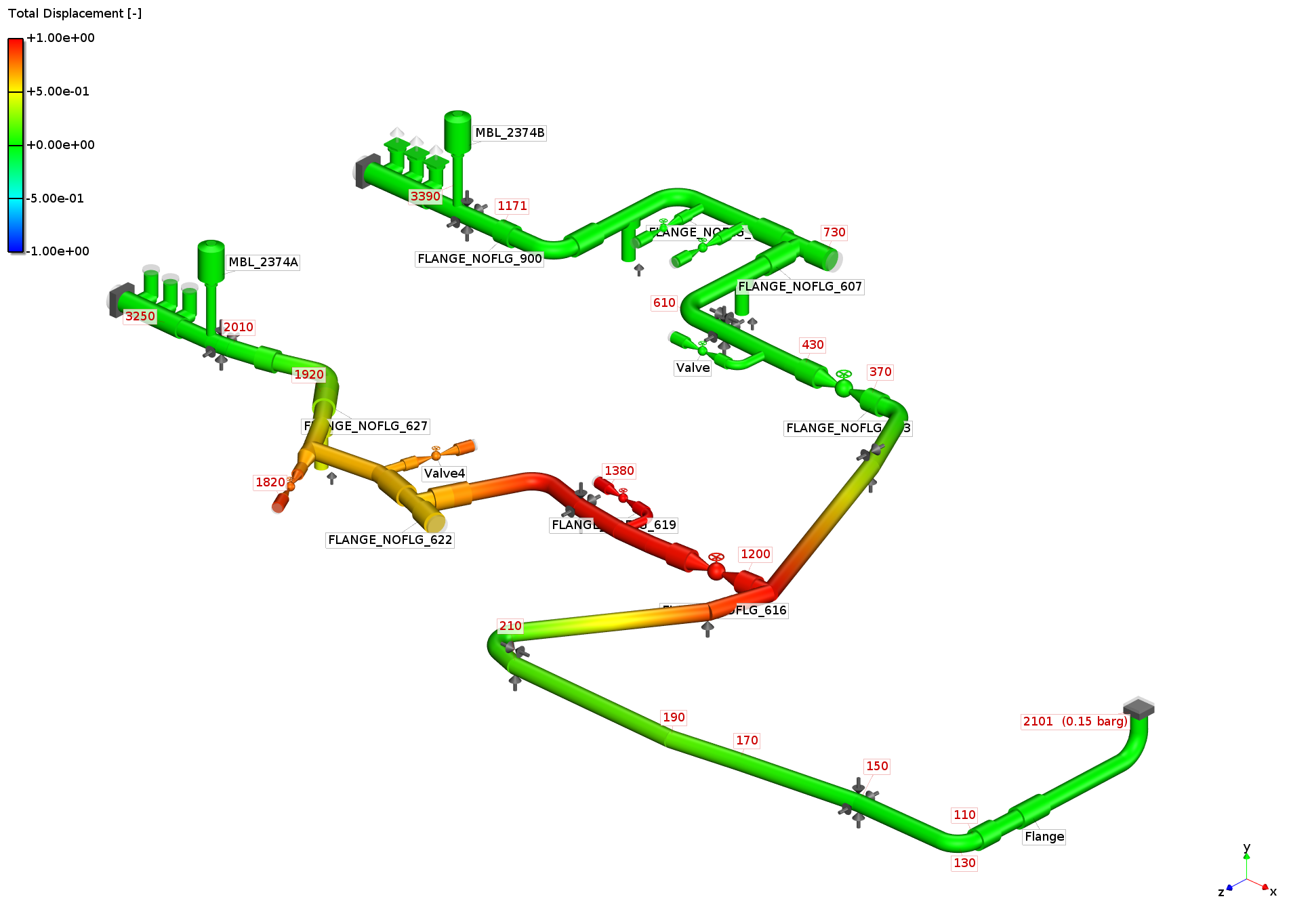
1 st Mode @ 13.3 Hz
Analysis: Modal
analysis of piping system (Piping Natural Frequencies)